Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress.
Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted to be the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade, also known as the great apes. The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, and Homo sapiens (modern human) are believed to have originated in Africa 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. In the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE Ancient Egypt, Kerma, Punt, and the Tichitt Tradition emerged in North, East and West Africa, while from 3000 BCE to 500 CE the Bantu expansion swept from modern-day Cameroon through Central, East, and Southern Africa, displacing or absorbing groups such as the Khoisan and Pygmies. Some African empires include Wagadu, Mali, Songhai, Sokoto, Ife, Benin, Asante, the Fatimids, Almoravids, Almohads, Ayyubids, Mamluks, Kongo, Mwene Muji, Luba, Lunda, Kitara, Aksum, Ethiopia, Adal, Ajuran, Kilwa, Sakalava, Imerina, Maravi, Mutapa, Rozvi, Mthwakazi, and Zulu. Despite the predominance of states, many societies were heterarchical and stateless. Slave trades created various diasporas, especially in the Americas. From the late 19th century to early 20th century, driven by the Second Industrial Revolution, most of Africa was rapidly conquered and colonised by European nations, save for Ethiopia and Liberia. European rule had significant impacts on Africa's societies, and colonies were maintained for the purpose of economic exploitation and extraction of natural resources. Most present states emerged from a process of decolonisation following World War II, and established the Organisation of African Unity in 1963, the predecessor to the African Union. The nascent countries decided to keep their colonial borders, with traditional power structures used in governance to varying degrees. (Full article...)
Selected article –
The Antemoro (or Antaimoro, lit. 'people of the shore') are an ethnic group of Madagascar living on the southeastern coast, mostly between Manakara and Farafangana. The name of tribe means From Imoro. Imoro is an historical name for the homeland of the Antemoro.Numbering around 500,000, this ethnic group mostly traces its origins back to East African Bantu and Indonesian Austronesian speakers like most other Malagasy. A minority of them belonging to the Anteony (aristocrats), Antalaotra (scribes of the Sorabe alphabet) or Anakara clans claim being descendants of settlers who arrived from Arabia, Persia and the Islamic religion was soon abandoned in favor of traditional beliefs and practices associated with respect for the ancestors, although remnants of Islam remain in fady such as the prohibition against consuming pork. In the 16th century an Antemoro kingdom was established, supplanting the power of the earlier Zafiraminia, who descended from seafarers of Sumatran origin.
The Antemoro (Anteony clan) soon developed a reputation as powerful sorcerers and astrologers, in large part owing to their monopoly on knowledge of writing, termed sorabe, which uses the Arabic script to transcribe the Malagasy language. Antemoro ombiasy (astrologer sages) migrated throughout the island, where they practiced their arts for local communities, served as advisers to kings, and even founded new principalities. This Antemoro mobility and their creation of a network of powerful spiritual advisers across the island is credited with forcing an awareness among Malagasy of communities beyond their own and sparking a sense of a common Malagasy identity. The Antemoro kingdom was disbanded in the late 19th century following an uprising of the Antemoro commoners against the noble class. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that Muhsin Hendricks of South Africa has been described as "the world's first openly gay imam"?
- ... that Albert Luthuli was the first African to win the Nobel Peace Prize?
- ... that the Philippine embassy in Pretoria responded to a South African newspaper's denunciation of horse fighting in the Philippines by saying that the practice was already illegal?
- ... that land for a library built for African Americans in Virginia was donated by Pope Pius XII?
- ... that women seeking abortions in Eswatini or in Lesotho may travel to neighbouring South Africa, where it is legal?
- ... that when South African anti-apartheid activist Kay Moonsamy went into exile, it was fifteen years before he saw his wife and children again?
Categories
Selected biography –
Mbaye Diagne (18 March 1958 – 31 May 1994) was a Senegalese military officer who served in Rwanda as a United Nations military observer from 1993 to 1994. During the Rwandan genocide, he undertook many missions on his own initiative to save the lives of civilians.
Diagne was born in Senegal. After graduating from the University of Dakar, he enrolled in the Senegalese Army's École Nationale des Officiers d'Active. He completed his schooling the following year and eventually attained the rank of captain. He was given command of the 3rd Company of the 6th Infantry Battalion and fought in the Casamance conflict from 1989 to 1993. (Full article...)
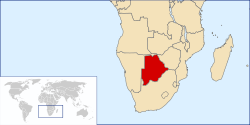
Selected country –
 |

|
|
| ||
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana (Tswana: Lefatshe lo Botswana), is a landlocked nation in Southern Africa. Citizens of Botswana are Batswana (singular: Motswana), regardless of ethnicity. Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent within the Commonwealth on 30 September 1966. Bordered by South Africa to the south and southeast, Namibia to the west, Zambia to the north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast, it is divided into nine districts, which are further subdivided into a total twenty-eight subdistricts.
For over 30 years, Botswana had the fastest growing economy in the world, with growth averaging over 9% per year from 1966 to 1999. The economy, closely tied to South Africa's, is dominated by mining (38 percent), services (44 percent), construction (7 percent), manufacturing (4 percent) and agriculture (2 percent). Botswana has been hit very hard by the AIDS epidemic; the average life expectancy in Botswana at birth has declined from 64 years in 1990 to 50.6 years in 2007. (Read more...)
Selected city –

Fes (/fɛs/; Arabic: فاس, romanized: fās) or Fez (/fɛz/) is a city in northern inland Morocco and the capital of the Fez-Meknes administrative region. It is one of the largest cities in Morocco, with a population of 1.256 million, according to the 2024 census. Located to the northwest of the Atlas Mountains, it is surrounded by hills and the old city is centered around the Fez River (Oued Fes) flowing from west to east. Fez has been called the "Mecca of the West" and the "Athens of Africa". It is also considered the spiritual and cultural capital of Morocco.
Founded under Idrisid rule during the 8th–9th centuries CE, Fez initially consisted of two autonomous and competing settlements. Successive waves of mainly Arab immigrants from Ifriqiya (Tunisia) and al-Andalus (Spain/Portugal) in the early 9th century gave the nascent city its Arab character. After the downfall of the Idrisid dynasty, other empires came and went until the 11th century when the Almoravid Sultan Yusuf ibn Tashfin united the two settlements into what is today's Fes el-Bali (lit. 'Old Fes') quarter, a.k.a. Medina of Fez. Under Almoravid rule, the city gained a reputation for religious scholarship and mercantile activity. (Full article...)
In the news
- 24 April 2025 – Somali Civil War
- Al-Shabaab militants seize the town of Wargaadhi and its military base in Middle Shabelle, Somalia. More than 40 militants and twelve clan fighters are killed in related combat. (Al Jazeera)
- 24 April 2025 – Islamist insurgency in the Sahel
- The Beninese government announces that 54 soldiers were killed in an attack by Jama'at Nasr al-Islam wal Muslimin (JNIM) in the north of the country last week, after previously announcing only eight soldiers were killed. JNIM claims 70 soldiers were killed in the attack. (BBC)
- 22 April 2025 –
- Interpol rescues 33 West Africans, including people from Benin, Togo, Burkina Faso, and Ghana, from human trafficking rings in the Ivory Coast. (AP)
- 21 April 2025 – Spillover of the Sudanese civil war
- 2025 Nasir clashes
- The South Sudan People's Defence Forces capture the town of Nasir in Upper Nile State from the Nuer White Army. (Reuters)
- 21 April 2025 – Boko Haram insurgency
- The Islamic State claims responsibility for a series of deadly attacks targeting Christians and security forces in Borno and Adamawa, Nigeria earlier this month that killed at least nine people and injured several others. (Reuters)
Updated: 5:05, 26 April 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –

- ... that the British Museum's oldest African-American object is the Akan Drum (pictured) that was used to "dance the slaves"?
- ... that L.C. Lecesne rose to prominence as an activist against slavery after the British Government compensated him for his illegal exile from Jamaica?
- ... that despite receiving a budget allocation in 2003, the public sports stadium in Gibeon, Namibia, hadn't been repaired as of December 2007?
- ... that Thomas Edward Wilkinson was made Bishop of Zululand after his predecessor in South Africa, John Colenso, was excommunicated?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus